Greenhouse Gas Emission
What Are Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
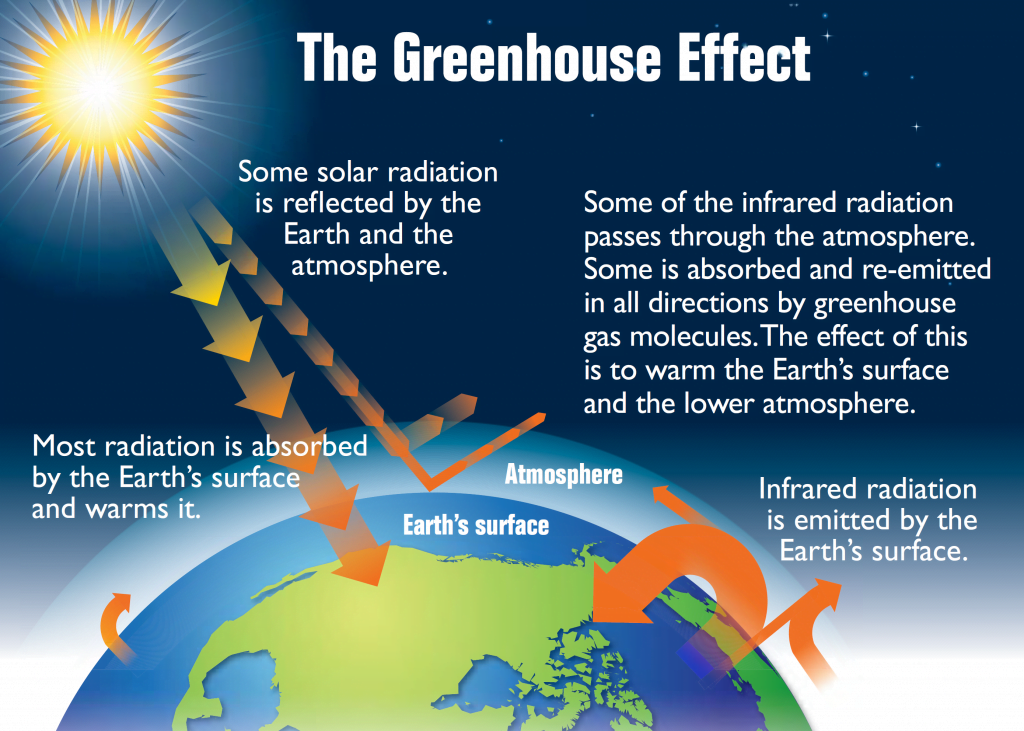
Greenhouse gas emissions are the release of gases like carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide into the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases act like a “greenhouse” by trapping energy from the sun. This trapped energy makes the Earth’s atmosphere warm, and disturbs the Earth’s climate.
What are the main causes of greenhouse gas emission
The main sources of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States are electricity generation, transportation, industry, and agriculture. Greenhouse gas emissions can be measured in different ways, including metric tons of CO2 equivalent (mtCO2e) or pounds of CO2 emitted.
Greenhouse gases effects
Greenhouse gas emissions have both short-term and long-term effects on the environment. The most direct short-term effect is global warming, which can cause sea levels to rise, extreme weather conditions, and changes in plant and animal habitats. Long-term effects include the potential for catastrophic climate change, which could lead to large-scale extinctions and global food shortages.
Greenhouse gases have a warming effect on the planet, which can lead to climate change. Some of the most common greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor. The effects of climate change can be wide-ranging and devastating, including increased flooding, drought, and food insecurity.
Greenhouse gas emissions are a major contributor to climate change, and it’s important to understand what they are and how they’re calculated. In this article, we’ll discuss the definition of greenhouse gas emissions, how they’re measured, and their effects on the environment. We’ll also look at some ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in your everyday life.
How are greenhouse gas emissions calculated?
Greenhouse gas emissions are measured by how much pollution is being released into the atmosphere. They are calculated by measuring the volume of greenhouse gases emitted and multiplying it by the associated emission factor.
How to calculate co2 emissions from fuel consumption
One important thing to note is that not all greenhouse gases are created equal. For example, methane has a much stronger global warming potential than carbon dioxide. So, even though there may be less methane emitted, it can have a much bigger impact on the environment.
There are a number of different ways of calculating greenhouse gas emissions. One popular method is to use the carbon dioxide equivalence or CO2e. This takes into account all the greenhouse gases and calculates their global warming potential. Another way of measuring emissions is in terms of metric tons.
How many greenhouse gases are there?
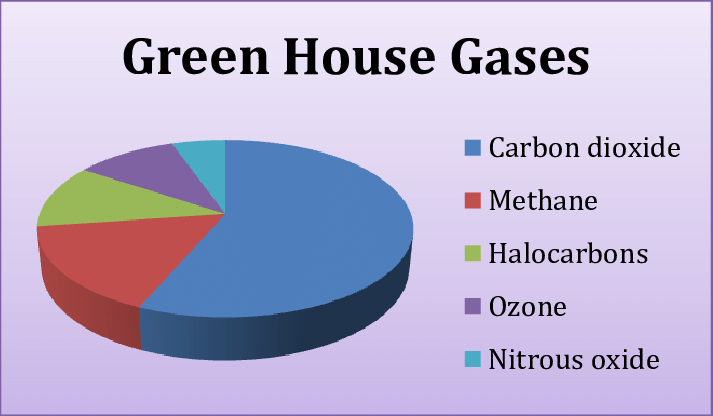
There are a number of different greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). The most common way of measuring greenhouse gas emissions is in terms of CO2 equivalent, or MMT CO2e. This takes into account the various greenhouse gases and calculates their global warming potential.
How do you calculate emission factor?
There are a number of different ways to calculate greenhouse gas emissions, but the most common is by determining the emission factor. The emission factor is a measure of how much CO2 is released per unit of fuel burned. To calculate CO2 emissions from natural gas, you would use the emission factor for natural gas, which is 0.00195 kg of CO2 per kWh.
When calculating greenhouse gas emissions, it is important to use the correct emission factor. This is a measure of how much greenhouse gas is released per unit of fuel consumed. For example, the emission factor for petrol is 2.3 kg CO2/litre. So, if you burn 10 litres of petrol, you will release 23 kg of CO2 into the atmosphere.







I was very pleased to uncover this site. I wanted to thank you for ones time for this particularly wonderful read!! I definitely liked every bit of it and I have you bookmarked to see new stuff on your blog.